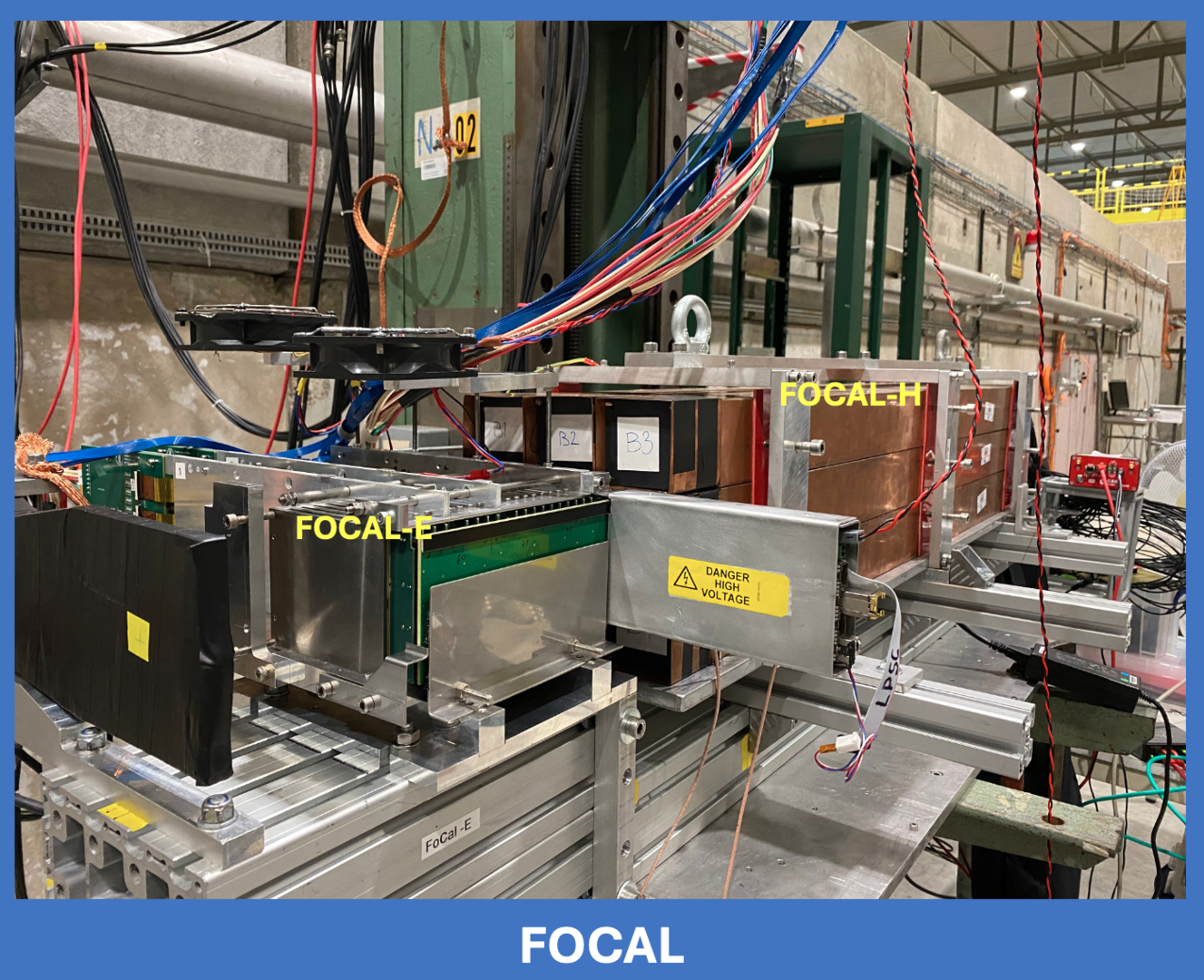
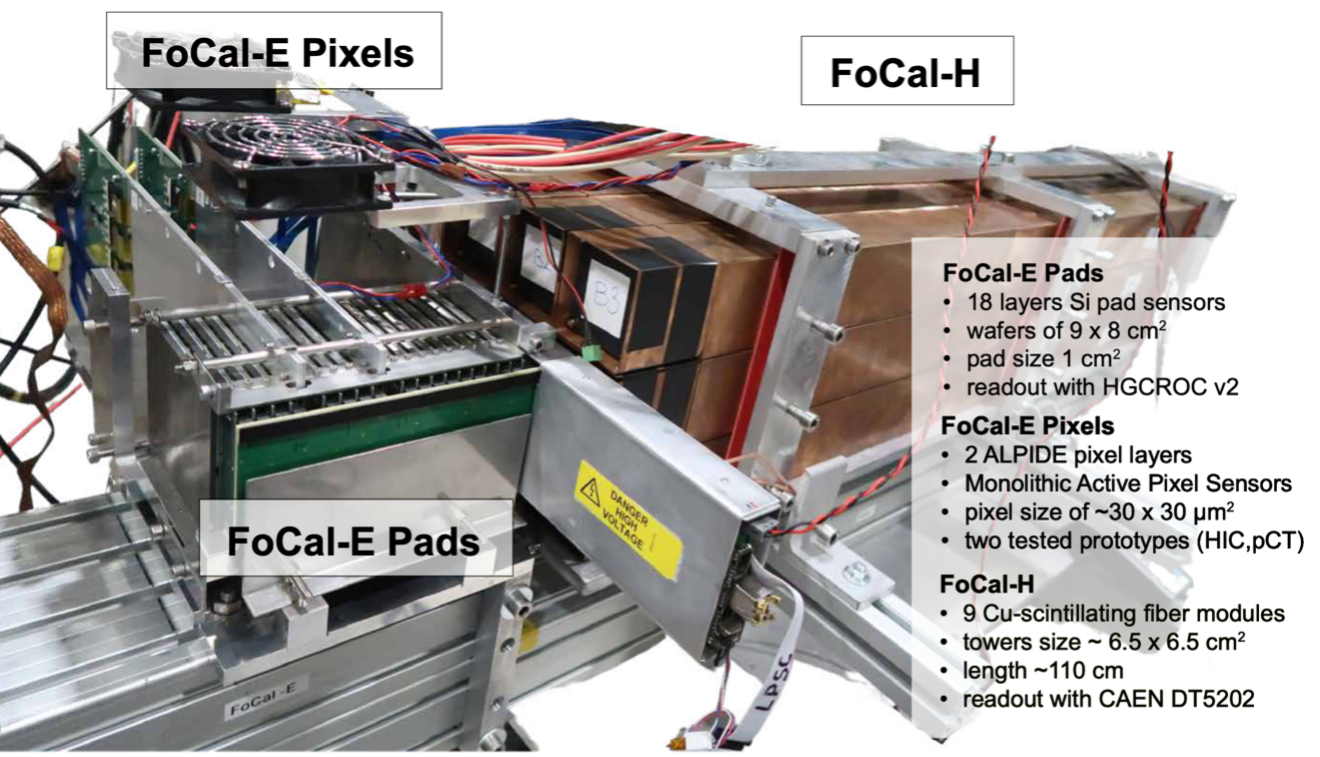
The forward electromagnetic and hadronic calorimeter (FoCal) is an upgrade to the ALICE experiment, to be installed during LS3 for data-taking in 2027–2029 at the LHC. The FoCal is a highly granular Si+W electromagnetic calorimeter combined with a conventional sampling hadronic calorimeter covering pseudorapidities of 3.4<η<5.8. The FoCal provides unique capabilities to measure small-x gluon distributions via prompt photon production and will significantly enhance the scope of ALICE for inclusive and correlation measurements with mesons, photons, and jets to explore the dynamics of hadronic matter at small x down to about 10-6.
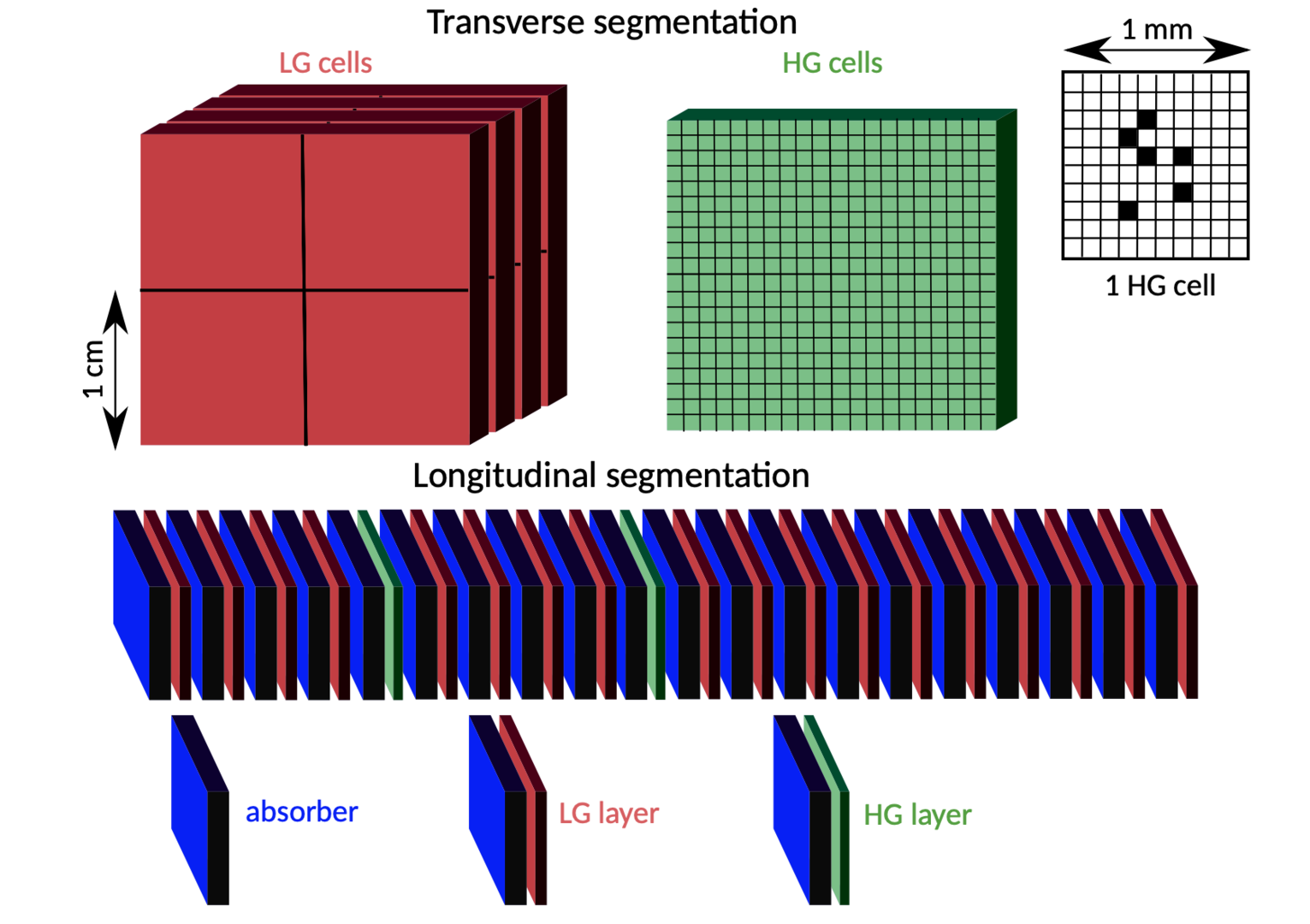
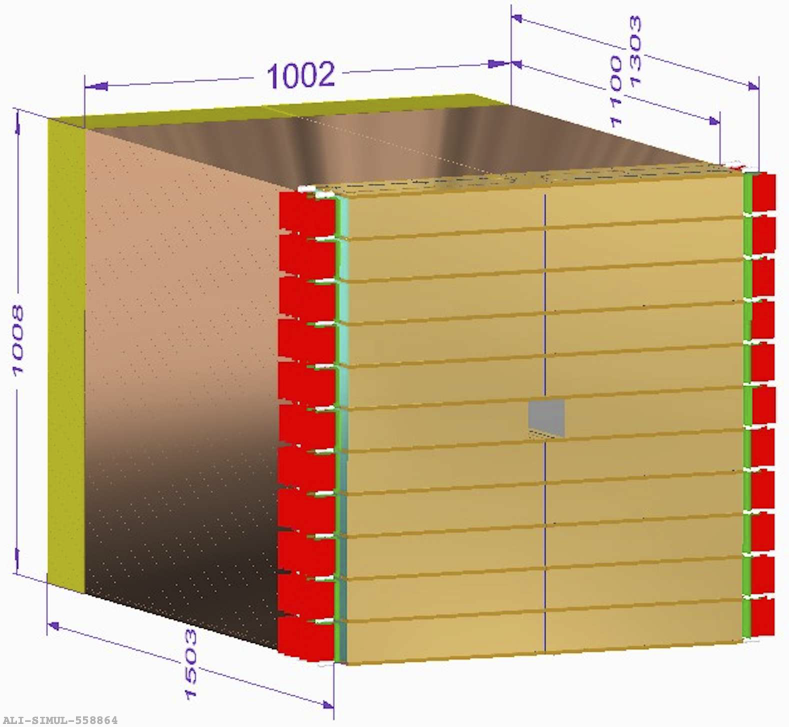
The FoCal-E detector will consist of a Si+W sampling calorimeter hybrid design using two different Si readout technologies:
- Pad layers, with transverse cell sizes of ≈ 1cm2
- Pixel layers, with digital readout and a cell size of ≈ 30×30μm2.
All layers will consist of W sheets of ≈ 1X0 followed by silicon sensors. The figure schematically shows the FoCal-E structure with 18 pad layers and two pixel layers, positioned at the 5th and 10th layer.
The electromagnetic calorimeter of FoCal will be complemented with a hadronic calorimeter (FoCal-H), which is needed for photon isolation and jet measurements.
More details in the ALICE FoCal Documentation page
FOCAL in the News
|
Documents
|
Internal
|